Versatile & Efficient Assistants
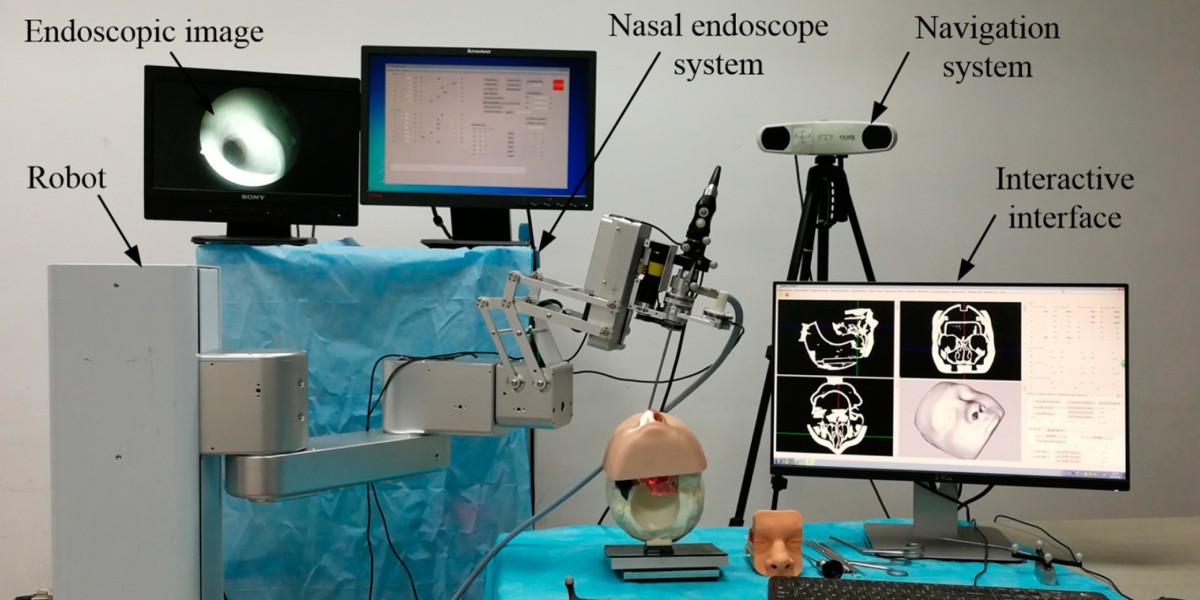
Endoscopes
Endoscopes or Endoscopy are versatile medical instruments that doctors use to perform a variety of diagnostic and surgical procedures. The procedures using endoscopes are minimally invasive. The doctors work by viewing the inside of a patient’s body through a thin, flexible tube and the camera at the end. Endoscopes in use today can range from the relatively simple to the very complex. They vary in size, cost, and scope. The most basic type, the rigid endoscope, is made of a rigid plastic tube. More complex types include semi-rigid, flexible, and semi-flexible endoscopes. Accessories such as magnifying lenses and light sources can be used to improve functionality.
Endoscopes Models
Without the proper equipment, doctors are sometimes unable to see inside you. When there’s a condition that needs to be identified or one that needs monitoring, doctors need special tools to see what’s going on. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like device that is inserted into the body through a small opening. Doctors can then use the endoscope to see what’s going on. There are several different sorts of endoscopes, each used for different types of care.
Types of Endoscopes
Endoscopes are classified based on the area or the organ of the body to be investigated. According to the American Cancer Society (ASC), some of the following types of endoscopes are listed below:
- Arthroscopy: The area targeted is joints and it is examined by Orthopaedic Surgeon.
- Bronchoscopy: investigated by pulmonologist or thoracic surgeon to view lings, trachea, and windpipe
- Colonoscopy: A Gastroenterologist or Proctologist will investigate the colon area.
- Cystoscopy: Urologist will target the area inside the bladder.
- Enteroscopy: A Gastroenterologist will conduct an examination to view the small intestine.
- Gastroscopy: A Gastroenterologist will investigate the Stomach and Duodenum.
- Hysteroscopy: It helps in investigating the inside of the uterus by Gynaecologists or Gynaecological Surgeons.
- Laparoscopy: Abdominal or pelvic area investigation is performed by various surgeons.
- Laryngoscopy: ENT specialists or Otolaryngologists examine the Larynx.
- Mediastinoscopy: Mediastinum, (area between the lungs) is investigated by a thoracic surgeon.
- Sigmoidoscopy: Gastroenterologist or Proctologist investigate Sigmoid Colon (lower part of the large intestine leading to rectum).
- Thoracoscopy or Pleuroscopy: The area between the lungs and the chest are investigated by a Pulmonologist or a Thoracic Surgeon.
- Ureteroscopy: Urologist will examine the Ureter.
How Endoscopes Work?
The endoscope examines the internal part of the body by inserting it into the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, or rectum. An endoscope consists of an eyepiece, a fibre optic cable that transmits the image from the device to a monitor, and a video camera. The endoscope helps to diagnose a disease or to perform surgery. With the help of an endoscope, the doctor can examine a patient’s internal area without making a large hole in the body.
The main uses of the endoscope include investigating the symptoms, diagnosing to determine for the disease and conditions, and treating problems or conditions.
Testing Image or Lens Quality in Endoscopes
The Lens of the endoscope and the fibre optic transmission play a critical role in the output of the endoscopes.
It becomes important to verify the image quality of the endoscopes periodically and also check for any cracks /moisture/dirt on the lens , which may interfere with the image quality.
Certain testing devices , are Specifically designed to ascertain & verify image and lens quality in endoscopes.
Visit www.helixindia.com for more details on these endoscope testing devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, endoscopes take doctors’ capabilities to the next level and allow diagnosing patients with precision.
With progress in the medical field, and the revolution in medical technology, the future of endoscopy looks bright.